Coupling of Artificial Atoms to V-groove Plasmonic Waveguides
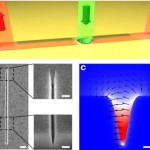
Figure: (a) Schematic of the considered configuration. A single nanodiamond hosting a single nitrogen vacancy (NV) center is placed inside a V-groove channel waveguide. On excitation with a laser, the NV center couples, in the ideal case, all of its emission into the VG-supported CPP mode. The channeled emission out-couples from the VG via the tapered nanomirrors at the VG extremities. (b) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of a 10-mm- long V-shaped groove (B315-nm-width and B510-nm-depth) fabricated by milling a thick gold film with a FIB. The scale bar is 1 mm. (c) Total electric field profile of the VG-supported CPP mode for a wavelength of 650 nm.
Article: published in Nature Communications by Carlos González Ballestero, Esteban Moreno and Prof. Francisco J. García Vidal, Department of Theoretical Condensed Matter Physics and IFIMAC researchers.
Department of Theoretical Condensed Matter Physics and IFIMAC – Condensed Matter Physics Center researchers report on deterministic coupling of single quantum emitters with channel plasmons
One of the main challenges in developing future nanoscale quantum photonic circuits is to manage combining on a single chip a single photon source, waveguides, modulators and detectors. An important milestone towards this ultimate goal is the deterministic coupling of a single quantum emitter to an integrated waveguide. In this context, IFIMAC researchers Carlos González Ballestero and Esteban Moreno lead by Prof. Francisco J. García Vidal, in collaboration with scientists from ICFO in Barcelona (Romain Quidant´s group), Denmark (Sergey Bozhevolnyi’s group) and United Kingdom (Yuri Alaverdyan), have been able to demonstrate coupling of the emission of a single quantum emitter to channel plasmons polaritons (CPPs) in a V-shaped plasmonic architecture. The study “Coupling of individual quantum emitters to channel plasmons”, has been published recently in the journal Nature Communications.
In this work, the researchers first used theoretical simulations to study the behaviour of the coupling between a quantum emitter and the V-groove plasmonic channel. Once an optimal theoretical configuration was identified, they used state-of-the-art techniques to assemble the experiment using a single Nitrogen Vacancy (NV) centre, a single quantum emitter present in diamond, coupled to the CPPs supported by a V-groove (VG) channel. The observations obtained from the experiment revealed efficient coupling of the NV centre emission to the propagating modes of the VG, in accordance with the theoretical predictions postulated by the team. This demonstrates that their approach can enable realistic and functional plasmonic circuitry and therefore, paves the way towards the development of efficient and long distance transfer of energy in integrated solid-state quantum systems. [Full article]