A Single Hydrogen Molecule as an Intensity Chopper in an Electrically Driven Plasmonic Nanocavity
Article: published in Nano Letters by César González Pascual, IFIMAC researcher and member of the Department of Theoretical Condensed Matter Physics.
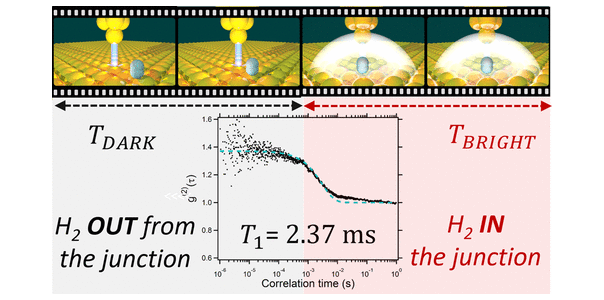
Photon statistics is a powerful tool for characterizing the emission dynamics of nanoscopic systems and their photophysics. Recent advances that combine correlation spectroscopy with scanning tunneling microscopy induced luminescence (STML) have allowed the measurement of the emission dynamics from individual molecules and defects, demonstrating their nature as single-photon emitters. The application of correlation spectroscopy to the analysis of the dynamics of a well-characterized adsorbate system in an ultrahigh vacuum remained to be demonstrated. Here, we combine single-photon time correlations with STML to measure the dynamics of individual H2 molecules between a gold tip and an Au(111) surface. An adsorbed H2 molecule performs recurrent excursions below the tip apex. We use the fact that the presence of the H2 molecule in the junction modifies plasmon emission to study the adsorbate dynamics. Using the H2 molecule as a chopper for STM-induced optical emission intensity, we demonstrate bunching in the plasmonic photon train in a single measurement over 6 orders of magnitude in the time domain (from microseconds to seconds) that takes only a few seconds. Our findings illustrate the power of using photon statistics to measure the diffusion dynamics of adsorbates with STML. [Full article]