Cooling By Cooper Pair Splitting
Article: published in Physical Review B selected as an “Editor’s Suggestion” paper by Rafael Sánchez and Alfredo Levy Yeyati, IFIMAC researchers and members of the Department of Theoretical Condensed Matter Physics.
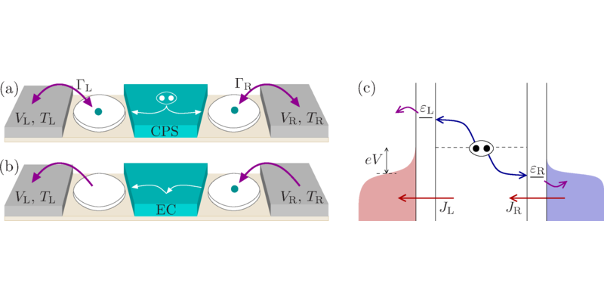
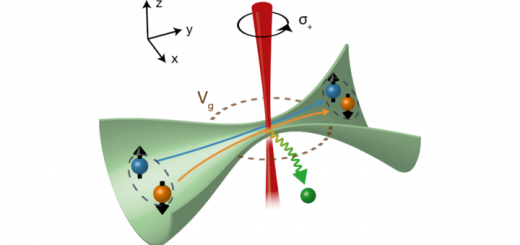
The electrons forming a Cooper pair in a superconductor can be spatially separated preserving their spin entanglement by means of quantum dots coupled to both the superconductor and independent normal leads. We investigate the thermoelectric properties of such a Cooper pair splitter and demonstrate that cooling of a reservoir is an indication of nonlocal correlations induced by the entangled electron pairs. Moreover, we show that the device can be operated as a nonlocal thermoelectric heat engine. Both as a refrigerator and as a heat engine, the Cooper pair splitter reaches efficiencies close to the thermodynamic bounds. As such, our work introduces an experimentally accessible heat engine and a refrigerator driven by entangled electron pairs in which the role of quantum correlations can be tested. [Full article]